Height rank
Post Turm
Bonn
- CVU Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Vertical Urbanism (CVU) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CVU floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.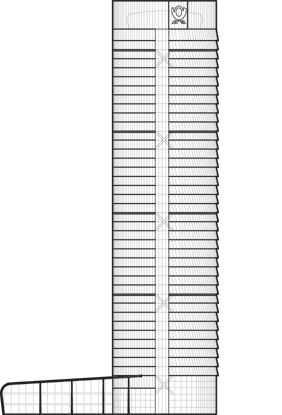
Official Name
Post Turm
Other Names
Deutsche Post Tower
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2002
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CVU "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CVU database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Composite
Height
162.5 m / 533 ft
Floors Above Ground
42
Floors Below Ground
5
# of Parking Spaces
450
# of Elevators
19
Tower GFA
107,000 m² / 1,151,738 ft²
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
Owner
Deutsche Post Bauen
Developer
Deutsche Post AG
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
Heinle, Wischer und Partner
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Brandi Consult GmbH
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
HOCHTIEF Construction AG Niederlassung Hamburg
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
HALFEN; Kuraray
Schindler; Sematic S.r.l.
Sika Services AG
CVU Awards & Distinctions
10 Year Award 2014 Winner
2014 CVU Awards
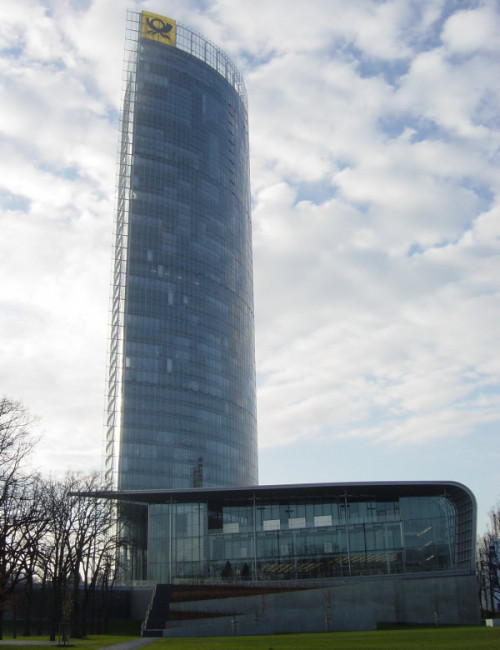
About Post Turm
Deutsche Post DHL’s Bonn headquarters is an expression of the company’s confidence in progress and in technology to improve the work environment. The architect’s aim was to create a forward-looking high-rise for the 21st century: formally, technically, and ecologically advanced, and offering a high quality work environment.
The Post Tower demonstrates the potential for technically integrated buildings to deliver high performance. From the onset of planning, the client expressed a strong desire to give all office staff direct access to the outside air and natural light. Combining these factors lead the design team to develop the twin-shell façade and split-building typology that embraces natural ventilation and green energy sources.
The Post Tower uses natural ventilation and decentralized cooling/heating systems to reduce the mechanical load, and consequently energy consumption, while improving floor-plate efficiency and eliminating mechanical shafts and ceiling ducts. This allows the tower to consume only 75 kWh/m2 (measured through 2003), which represents a 79 percent energy reduction when compared to a typical air-conditioned building. Only 3 kWh/m2 are used for cooling, and the energy used for heating is drastically reduced compared to the benchmark building. The savings on energy usage and central air-conditioning system equipment and space offset the additional investment in the façade.
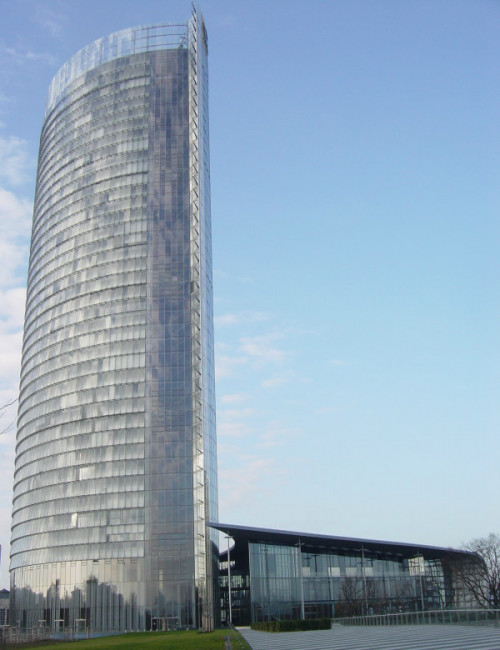
The Tower’s form consists of two, offset elliptical segments separated from each other by a 7.2 meter wide atrium that faces west towards the City of Bonn, and east towards the Rhine River. The atrium runs the full height of the Tower, incorporating the glazed passenger elevators, and it is divided into four parts by sky gardens; three are nine stories high and the top one is eleven. In each elliptical segment, cellular offices wrap around the perimeter, with conference rooms and core functions located towards the atrium. The two main façades of the high-rise face north and south, while the sky garden façades have east and west orientations. By orienting the building in the primary wind direction, the wind profile was optimized, both for structural efficiency and natural ventilation.
Outside air enters the building through the twin-shell façade, flows through the offices and into the corridors, which act as horizontal exhaust air collectors, ultimately venting the exhaust air into the atrium. Using the stack effect, the exhaust air in the atrium is then vented through operable windows located high in the façade of each nine-story atrium, with low-level vents added to assist the natural airflow.
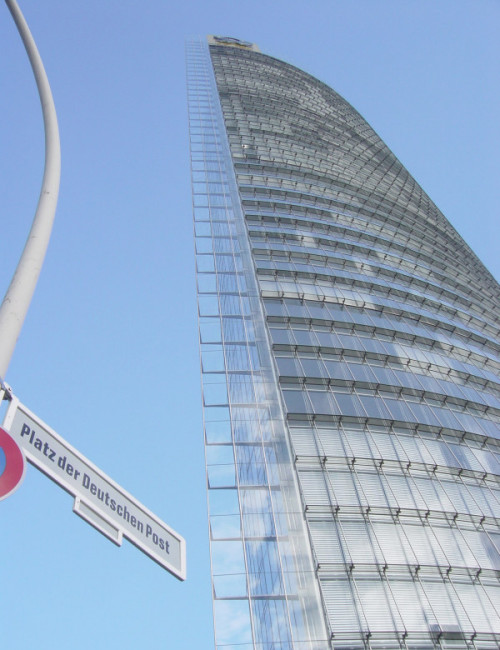
The façade consists of the outer single glazed façade, operable sunshades and an inner façade of floor- to-ceiling insulated glazing. The horizontal continuity of the façade and its aerodynamic shape allow it to dissipate the pressure differences across the faces of the building, enabling natural ventilation to take place without a draft.
The outer facade is hung in nine-story increments from extruded stainless steel mullions, and braced horizontally at every floor with wind needles. The south façade features sloped glass panes, allowing air-intake and exhaust at the bottom of each panel. The north facade is a smooth plane with alternating ventilation flaps.
The inner façade is a floor-to-ceiling aluminum curtain wall with insulated glazing. Motorized, operable windows are located in every other façade module. During spring and fall, these windows serve to naturally ventilate the offices, substantially reducing the building’s reliance on mechanical conditioning. After working hours, the windows are centrally opened to provide night flushing of the tower with cool air.
Each employee can manually alter the internal environment according to individual preferences using a touch-screen, allowing individual control of the blinds, lighting levels, operable windows, and internal temperatures.
The design of the Post Tower opened up new possibilities for the work environment, promoting interaction and communication, and delivering flexible spaces that can accommodate new layouts and technologies.
CVU Awards & Distinctions
10 Year Award 2014 Winner
2014 CVU Awards
Learn more about the Council on Vertical Urbanism
Discover how vertical living is shaping the next generation of urban environments. Explore insights, research, and global leadership in vertical urban development