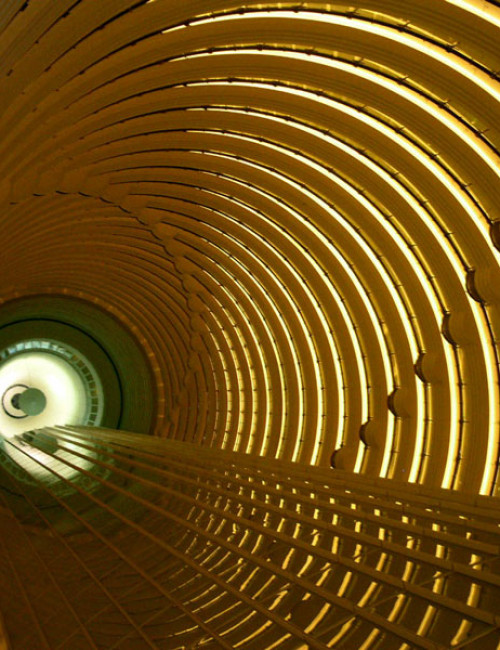
Height rank
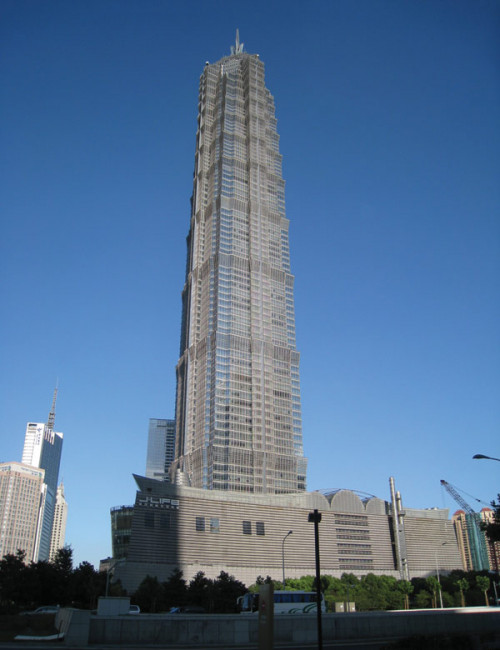
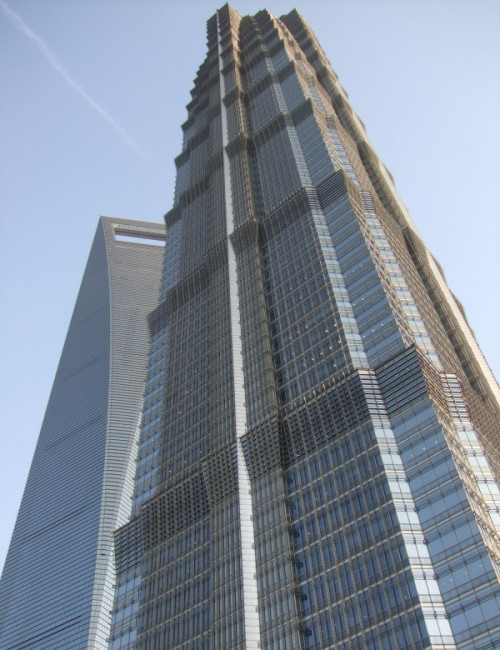
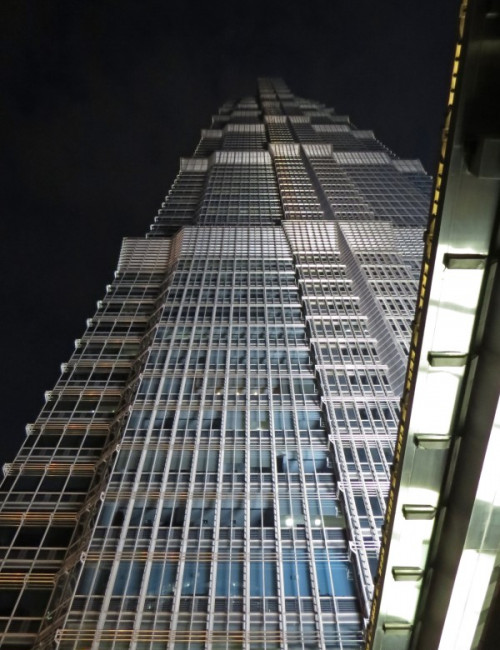
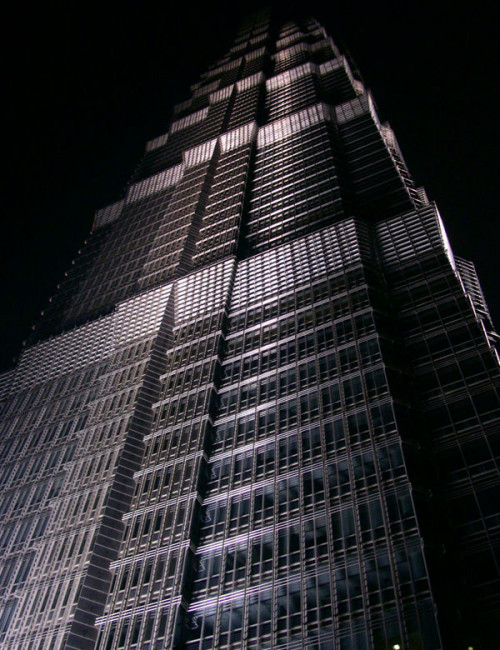
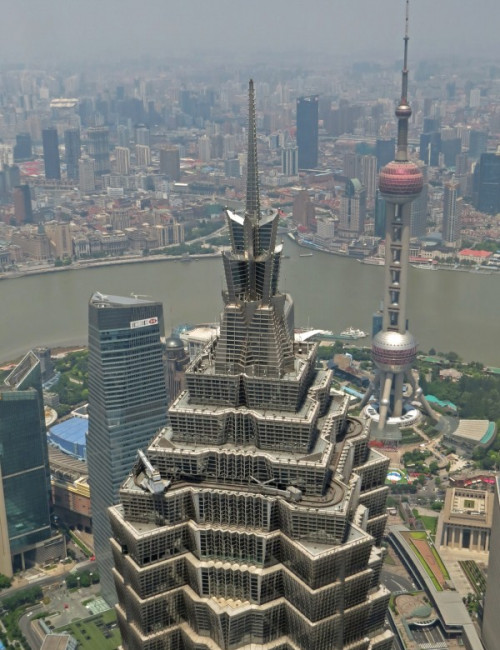
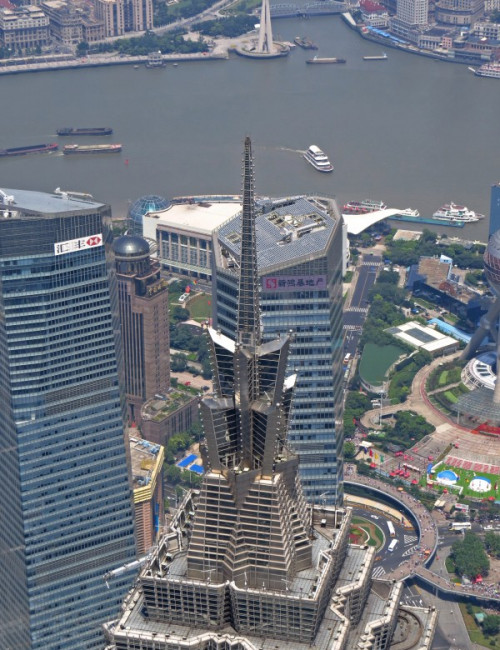
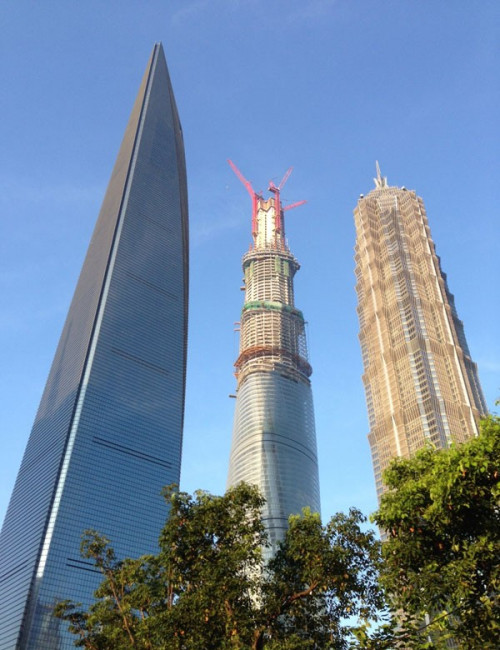
Jin Mao Tower
Shanghai
- CVU Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Vertical Urbanism (CVU) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.
Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CVU floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.Official Name
Jin Mao Tower
Other Names
Jin Mao Building
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
1999
Country
City
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CVU "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CVU database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Concrete-Steel Composite
Official Website
Height
420.5 m / 1,380 ft
Floors Above Ground
88
Floors Below Ground
3
# of Parking Spaces
993
# of Elevators
61
Top Elevator Speed
9 m/s
Tower GFA
289,500 m² / 3,116,152 ft²
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Retrofit Companies Involved
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CVU Member to view this resource.
Owner/Developer
China Jin Mao Group Co. Ltd
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
Shanghai Institute of Architectural Design & Research
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Engineer of Record takes the balance of the engineering effort not executed by the “Design Engineer,” typically responsible for construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc.
Shanghai Institute of Architectural Design & Research
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Shanghai Construction Group
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Shen Milsom Wilke, Inc.
PricewaterhouseCoopers
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Langdon & Seah
Edgett Williams Consulting Group Inc.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Armstrong World Industries
HALFEN
Mitsubishi Elevator and Escalator
AkzoNobel
Dow Corning Corporation
Arbed; Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation
Retrofit Companies Involved
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
CVU Awards & Distinctions
Performance Award 2014 Award of Excellence
2014 CVU Awards
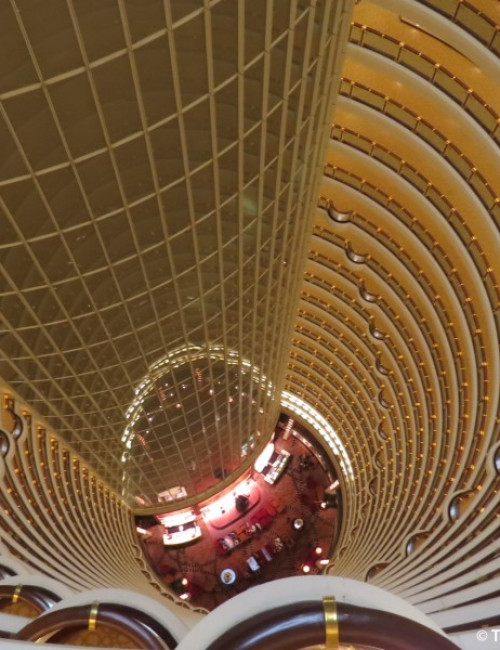
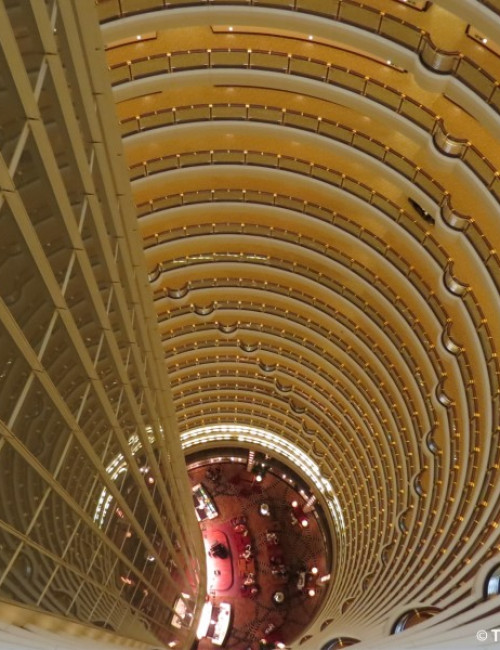
About Jin Mao Tower
The Jin Mao Tower, a mixed-use complex containing offices, convention space and a hotel and in 2013 became the tallest and the longest-operated building in China to receive a LEED-EB: OM (Existing Buildings: Operations + Management) Gold certification. Its high performance has been achieved with the assistance of a computerized energy management system, which has been in place since the building opened, and is integrated with the broader enterprise asset management (EAM) system.
Management tracks a variety of performance metrics, including electricity, water, and natural gas consumption from month to month, and maintains key performance indicators (KPIs) around non-energy metrics, such as preventative maintenance, fixed asset purchases, requests for repairs, complaints, cost analysis and equipment information records. The paperless processing associated with the system also contributes to the building’s low carbon-emission footprint. Beginning in August 2013, to promote indoor air quality (IAQ) the building’s managers began tracking PM 2.5 particulate values in office areas, and broadcasting the results daily on social media.
These performance measurement approaches have been augmented by consulting with the Association of German Engineers, which has helped Jin Mao develop computerized equipment management systems to help maintenance staff optimize the equipment life cycle, quality and cost. A fluid energy metering system measures the flow of water through 89 sensors distributed throughout the building. An electricity metering system remotely and automatically measures electricity consumption of large equipment through a network of 300 sensors, allowing comparison of current and historical energy consumption. Together, these systems provide an objective data foundation for energy-use analysis.
Each month, building managers hold an energy-consumption analysis meeting and clarify energy expenditure of each main equipment category, including water, electricity, and natural gas. The management team actively compares year-on-year and month-to-month consumption statistics, referencing the building automation system’s daily control log, to make informed decisions about where energy-saving strategies should be implemented next. Specific action items are then drawn up for specific people, who take charge of implementing these measures.
CVU Awards & Distinctions
Performance Award 2014 Award of Excellence
2014 CVU Awards
Learn more about the Council on Vertical Urbanism
Discover how vertical living is shaping the next generation of urban environments. Explore insights, research, and global leadership in vertical urban development